Video Colonoscopy
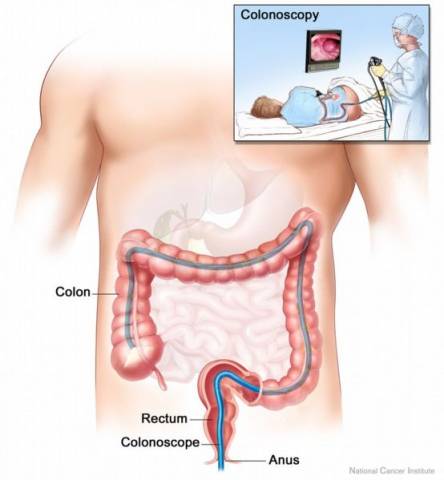
Video-Colonoscopy is an examination recommended for all persons over 40 years of age with or without symptoms. Used as a preventive medical diagnostic exam it has enabled the discovery of many colon cancers still at a treatable stage.
Doctor, why do I have to go to the Doctor for a Colonoscopy examination, if I don't have any symptoms at all?
Answer: You, myself or anybody are in risk of developing a colon or rectum cancer. We don't know for sure who will have it, but according to the American Association against Cancer, it is recommended to have a colonoscopy study every five years for a person over 40 years old.
The colon and rectum cancer are one of the most frequent and according to statistics, keeps growing, regardless of gender, but it is still the most preventive.
Which is the main purpose of this test?
Answer: The purpose is the detection of small tumors known as polyps, which could remain undetected and grow in the colon quietly for many years. Only some of them will show symptoms and/or some will develop cancer.
The main purpose of the test is to detect the cancer from the beginning o from the Polyp. Normally, when the cancer shows the symptoms it means that it is already in its advance stage; this is why the “complete colonoscopy” test should always be practice every 5 years, since this type of cancer is perfectly preventive.
It is also worthy to reflect upon the fact that when the rectum cancer is near the anus, the surgery performed is one of the worst things that could happen to a person, which is to have a colostomy for all his life. This means to defecate through a bag sticked to his abdomen.
Besides all this advantages, we have to add that a lot of people may get confuse and think they have hemorrhoids, and without consulting an specialist they make a mistake to get a self-treatment by using creams or suppositories for what they wrongly believe to be hemorrhoids, until they finally realize it is cancer.
Doctor, if you find through colonoscopy that I have a polip, how are we going to eliminate it?
Luckily we can remove it without open surgery, we relay on a very specialized equipment like the endoscopy polypectomy, through wich very often we can cut them, with no need of open surgery and by this procedure we will succeed in fighting a probable cancer. We also count on an argon plasma coagulator equipment which is combined with polypectomy that it is possible to eliminate any Polyps of any type and size.
Is the exam painful?
Answer: Nowadays we have a modern sedatives which are given by an anesthesiologist physician, therefore the patient has a very comfortable time, and after the procedure, The patient will remember nothing. In other words, any discomfort will be eliminated by sedatives or taken out the air that could get into the colon by the endoscopist using the colonoscopy equipment.
Preventive Technique
It is “absolutely recommended”, as a way of prevention, the practice of the colonoscopy with patients in risk of developing a colon cancer, moreover in family patients that have had a tumor in first degree, or in those having diseases related to a major incidence of this type of cancer.
“In this individuals, having an early colonoscopy could detect this small lesions that, once being remove, will prevent the development of colon cancer, in a short or middle term”. A colonoscopy prevents the occurrence of invasive carcinoma within 10 years, a data that justifies itself the expenses that involve taking the test”.
The colonoscopy is not currently a bothersome technique for the patient, which does not prevent them to recognize that, some years ago, when it was practiced without sedatives, it was, indeed.
“It can’t be planned any type of prevention strategy, to an asymptomatic person if they are not assure some degree of comfort during the practice of colonoscopy, or endoscopy. At present time, all the explorations take place with a very short period of sedation, as a result of what the patient has a quiet comfortable experience, along with the fact that the tubes are more flexible and the specialists are far more experienced. The endoscopies must be painless, based on the assumption that we can’t give pain to an asymptomatic patient”.
One of the main target of the perform a complete colonoscopy
is to find colon's polyps that some but not all benign neoplasic
polyps will transform into carcinomas the "theory adenoma- carcinoma". (The polyps can transform in a cancer from a period of two years to seven years and most of the times make no symptoms until advanced stages are reaches!)
If the polyps is or are founded can be removed easily by the procedure called polypectomy.
A colonoscopy is also necessary to:
Examine patients who test positive for blood in the stool.
Check inflammatory bowel disease (colitis)
Monitor patients with a past history of colon polyps or cancer
Bleeding lesions, bleeding may occur from different points in the colon
Chronic diarrhea, constipation, or a change in bowel habits
Anemia.
Preparation To obtain the full benefits of the exam, the colon must be clean and free of stool.
The patient receives instructions on how to do this. It involves drinking a solution which flushes the colon clean or taking laxatives and enemas. Usually the patient drinks only clear liquids and eats no food for the day before the exam. The physician advises the patient regarding the use of regular medications during that time.
The Procedure Colonoscopy is usually performed on an outpatient basis. The patient is mildly sedated, the endoscope is inserted through the anus and moved gently around the bends of the colon. If a polyp is encountered, a thin wire snare is used to lasso it. Electrocautery (electrical heat) is applied to painlessly remove it. Other tests can be performed during colonoscopy, including biopsy to obtain a small tissue specimen for microscopic analysis. The procedure takes 15 to 30 minutes and is seldom remembered by the sedated patient. A recovery area is available to monitor vital signs until the patient is fully awake. It is normal to experience mild cramping or abdominal pressure following the exam. This usually subsides in an hour or so.