Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
What is Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)?
Irritable bowel syndrome is a disorder characterized most commonly by cramping, abdominal pain, bloating, constipation, and diarrhea. IBS causes a great deal of discomfort and distress, but it does not permanently harm the intestines and does not lead to a serious disease, such as cancer. Most people can control their symptoms with diet, stress management, and prescribed medications. For some people, however, IBS can be disabling. They may be unable to work, attend social events, or even travel short distances.
As many as 20 percent of the adult population, or one in five Americans, has symptoms of IBS, making it one of the most common disorders diagnosed by doctors. It occurs more often in women than in men, and it begins before the age of 35 in about 50 percent of people.
What are the symptoms of IBS?
Abdominal pain, bloating, and discomfort are the main symptoms of IBS. However, symptoms can vary from person to person. Some people have constipation, which means hard, difficult-to-pass, or infrequent bowel movements. Often these people report straining and cramping when trying to have a bowel movement but cannot eliminate any stool, or they are able to eliminate only a small amount. If they are able to have a bowel movement, there may be mucus in it, which is a fluid that moistens and protect passages in the digestive system. Some people with IBS experience diarrhea, which is frequent, loose, watery, stools. People with diarrhea frequently feel an urgent and uncontrollable need to have a bowel movement. Other people with IBS alternate between constipation and diarrhea. Sometimes people find that their symptoms subside for a few months and then return, while others report a constant worsening of symptoms over time.
What causes IBS?
Researchers have yet to discover any specific cause for IBS. One theory is that people who suffer from IBS have a colon (large bowel) that is particularly sensitive and reactive to certain foods and stress. The immune system, which fights infection, may also be involved.
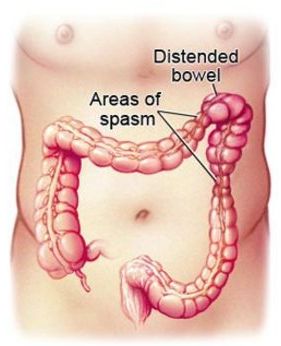
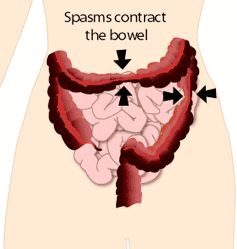
Normal motility, or movement, may not be present in a colon of a person who has IBS. It can be spasmodic or can even stop working temporarily. Spasms are sudden strong muscle contractions that come and go.
The lining of the colon called the epithelium, which is affected by the immune and nervous systems, regulates the flow of fluids in and out of the colon. In IBS, the epithelium appears to work properly. However, when the contents inside the colon move too quickly, the colon looses its ability to absorb fluids. The result is too much fluid in the stool. In other people, the movement inside the colon is too slow, which causes extra fluid to be absorbed. As a result, a person develops constipation.
A person's colon may respond strongly to stimuli such as certain foods or stress that would not bother most people.
Recent research has reported that serotonin is linked with normal gastrointestinal (GI) functioning. Serotonin is a neurotransmitter, or chemical, that delivers messages from one part of your body to another. Ninety-five percent of the serotonin in your body is located in the GI tract, and the other 5 percent is found in the brain. Cells that line the inside of the bowel work as transporters and carry the serotonin out of the GI tract. People with IBS, however, have diminished receptor activity, causing abnormal levels of serotonin to exist in the GI tract. As a result, people with IBS experience problems with bowel movement, motility, and sensation—having more sensitive pain receptors in their GI tract.
In addition, people with IBS frequently suffer from depression and anxiety, which can worsen symptoms. Similarly, the symptoms associated with IBS can cause a person to feel depressed and anxious.
Researchers have reported that IBS may be caused by a bacterial infection in the gastrointestinal tract. Studies show that people who have had gastroenteritis sometimes develop IBS, otherwise called post-infectious IBS.
Researchers have also found very mild celiac disease in some people with symptoms similar to IBS. People with celiac disease cannot digest gluten, a substance found in wheat, rye, and barley. People with celiac disease cannot eat these foods without becoming very sick because their immune system responds by damaging the small intestine. A blood test can determine whether celiac disease may be present. (For information about celiac disease, see NIDDK's Celiac Disease fact sheet.)
The following have been associated with a worsening of IBS symptoms
large meals
bloating from gas in the colon
medicines
wheat, rye, barley, chocolate, milk products, or alcohol
drinks with caffeine, such as coffee, tea, or colas
stress, conflict, or emotional upsets
Researchers have found that women with IBS may have more symptoms during their menstrual periods, suggesting that reproductive hormones can worsen IBS problems.
What does the colon do?
The colon, which is about 5 feet long, connects the small intestine to the rectum and anus. The major function of the colon is to absorb water, nutrients, and salts from the partially digested food that enters from the small intestine. Two pints of liquid matter enter the colon from the small intestine each day.
Stool volume is a third of a pint. The difference between the amount of fluid entering the colon from the small intestine and the amount of stool in the colon is what the colon absorbs each day.
Colon motility (the contraction of the colon muscles and the movement of its contents) is controlled by nerves, hormones, and impulses in the colon muscles. These contractions move the contents inside the colon toward the rectum. During this passage, water and nutrients are absorbed into the body, and what is left over is stool. A few times each day contractions push the stool down the colon, resulting in a bowel movement. However, if the muscles of the colon, sphincters, and pelvis do not contract in the right way, the contents inside the colon do not move correctly, resulting in abdominal pain, cramps, constipation, a sense of incomplete stool movement, or diarrhea.
How is IBS diagnosed?
If you think you have IBS, seeing your doctor is the first step. IBS is generally diagnosed on the basis of a complete medical history that includes a careful description of symptoms and a physical examination.
There is no specific test for IBS, although diagnostic tests may be performed to rule out other diseases. These tests may include stool sample testing, blood tests, and x rays. Typically, a doctor will perform a sigmoidoscopy, or colonoscopy, which allows the doctor to look inside the colon. This is done by inserting a small, flexible tube with a camera on the end of it through the anus.
The camera then transfers the images of your colon onto a large screen for the doctor to see better.
If your test results are negative, the doctor may diagnose IBS based on your symptoms, including how often you have had abdominal pain or discomfort during the past year, when the pain starts and stops in relation to bowel function, and how your bowel frequency and stool consistency have changed. Many doctors refer to a list of specific symptoms that must be present to make a diagnosis of IBS.
Symptoms include
Abdominal pain or discomfort for at least 12 weeks out of the previous 12 months. These 12 weeks do not have to be consecutive.
The abdominal pain or discomfort has two of the following three features:
- It is relieved by having a bowel movement.
- When it starts, there is a change in how often you have a bowel movement.
- When it starts, there is a change in the form of the stool or the way it looks.
Certain symptoms must also be present, such as
- a change in frequency of bowel movements
- a change in appearance of bowel movements
- feelings of uncontrollable urgency to have a bowel movement
- difficulty or inability to pass stool
- mucus in the stool
- bloating
Bleeding, fever, weight loss, and persistent severe pain are not symptoms of IBS and may indicate other problems such as inflammation, or rarely, cancer.
 What is the treatment for IBS?
What is the treatment for IBS?
Unfortunately, many people suffer from IBS for a long time before seeking medical treatment. Up to 70 percent of people suffering from IBS are not receiving medical care for their symptoms. No cure has been found for IBS, but many options are available to treat the symptoms. Your doctor will give you the best treatments available for your particular symptoms and encourage you to manage stress and make changes to your diet.
Medications are an important part of relieving symptoms. Your doctor may suggest fiber supplements or laxatives for constipation or medicines to decrease diarrhea, such as Lomotil or loperamide (Imodium). An antispasmodic is commonly prescribed, which helps to control colon muscle spasms and reduce abdominal pain. Antidepressants may relieve some symptoms. However, both antispasmodics and antidepressants can worsen constipation, so some doctors will also prescribe medications that relax muscles in the bladder and intestines, such as Donnapine and Librax. These medications contain a mild sedative, which can be habit forming, so they need to be used under the guidance of a physician.
Medications available specifically to treat IBS are:
Alosetron hydrochloride (Lotronex), which has been reapproved with significant restrictions by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for women with severe IBS who have not responded to conventional therapy and whose primary symptom is diarrhea. However, even in these patients,
Lotronex should be used with great caution because it can have serious side effects such as severe constipation or decreased blood flow to the colon.
Tegaserod maleate (Zelnorm), which has been approved by the FDA for the short-term treatment of women with IBS whose primary symptom is constipation. Zelnorm is prescribed for a standard 4 to 6 weeks.
If a person feels better and experiences a decrease in symptoms, the doctor may prescribe Zelnorm for an additional 4 to 6 weeks.
With any medication, even over-the-counter medications such as laxatives and fiber supplements, it is important to follow your doctor's instructions. Some people report a worsening in abdominal bloating and gas from increased fiber intake, and laxatives can be habit forming if they are used too frequently.
Medications affect people differently, and no one medication or combination of medications will work for everyone with IBS.
You will need to work with your doctor to find the best combination of medicine, diet, counseling, and support to control your symptoms.
How does stress affect IBS?
Stress—feeling mentally or emotionally tense, troubled, angry, or overwhelmed—can stimulate colon spasms in people with IBS. The colon has many nerves that connect it to the brain. Like the heart and the lungs, the colon is partly controlled by the autonomic nervous system, which responds to stress. These nerves control the normal contractions of the colon and cause abdominal discomfort at stressful times.
People often experience cramps or "butterflies" when they are nervous or upset. In people with IBS, the colon can be overly responsive to even slight conflict or stress. Stress makes the mind more aware of the sensations that arise in the colon, making the person perceive these sensations as unpleasant.
Some evidence suggests that IBS is affected by the immune system, which fights infection in the body. The immune system is affected by stress. For all these reasons, stress management is an important part of treatment for IBS.
Stress management options include
stress reduction (relaxation)
training and relaxation therapies such as meditation
counseling and support
regular exercise such as walking or yoga
changes to the stressful situations in your life
adequate sleep
Can changes in diet help IBS
For many people, careful eating reduces IBS symptoms. Before changing your diet, keep a journal noting the foods that seem to cause distress. Then discuss your findings with your doctor. You may want to consult a registered dietitian who can help you make changes to your diet. For instance, if dairy products cause your symptoms to flare up, you can try eating less of those foods. You might be able to tolerate yogurt better than other dairy products because it contains bacteria that supply the enzyme needed to digest lactose, the sugar found in milk products.
Dairy products are an important source of calcium and other nutrients. If you need to avoid dairy products, be sure to get adequate nutrients in the foods you substitute, or take supplements.
In many cases, dietary fiber may lessen IBS symptoms, particularly constipation. However, it may not help with lowering pain or decreasing diarrhea. Whole grain breads and cereals, fruits, and vegetables are good sources of fiber. High-fiber diets keep the colon mildly distended, which may help prevent spasms. Some forms of fiber keep water in the stool, thereby preventing hard stools that are difficult to pass.
Doctors usually recommend a diet with enough fiber to produce soft, painless bowel movements. High-fiber diets may cause gas and bloating, although some people report that these symptoms go away within a few weeks. (For information about diets for people with celiac disease, please see NIDDK's Celiac Disease fact sheet.) Increasing fiber intake by 2 to 3 grams per day will help reduce the risk of increased gas and bloating.
Drinking six to eight glasses of plain water a day is important, especially if you have diarrhea. Drinking carbonated beverages, such as sodas, may result in gas and cause discomfort. Chewing gum and eating too quickly can lead to swallowing air, which also leads to gas.
Large meals can cause cramping and diarrhea, so eating smaller meals more often, or eating smaller portions, may help IBS symptoms. Eating meals that are low in fat and high in carbohydrates such as pasta, rice, whole-grain breads and cereals (unless you have celiac disease), fruits, and vegetables may help.